University Social Responsibility (USR)
University Social Responsibility System of CSU
Based on the University’s Institutional Development Plan and the Higher Education Sprout Project: Innovative Practice, Cross-Disciplinary Integration, Local Engagement, and Global Alignment, Cheng Shiu University has mapped out its University Social Responsibility (USR) blueprint. With the vision of “Building a Sustainable Campus and Advancing a Thriving Local Community,” the University set dual goals of Sustainable Campus and Sustainable Community. Four action dimensions—Education, Economy, Culture, and Environment—were established to guide implementation. These core values of campus sustainability integrate regional and academic resources to foster community development, strengthen industrial clusters, and promote cultural innovation.
Overall USR Development Plan
As USR implementation and sustainability issues become increasingly diverse and complex, the Office of Social Responsibility and Sustainability has expanded its mandate to include campus sustainability promotion. The Office integrates USR initiatives with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), advancing mid- to long-term planning, innovative curriculum consultation, and faculty and partner community engagement. Through the publication of CSR yearbooks and sustainability reports, the University showcases its strengths while strengthening connections with stakeholders.
Cheng Shiu University USR Implementation Blueprint
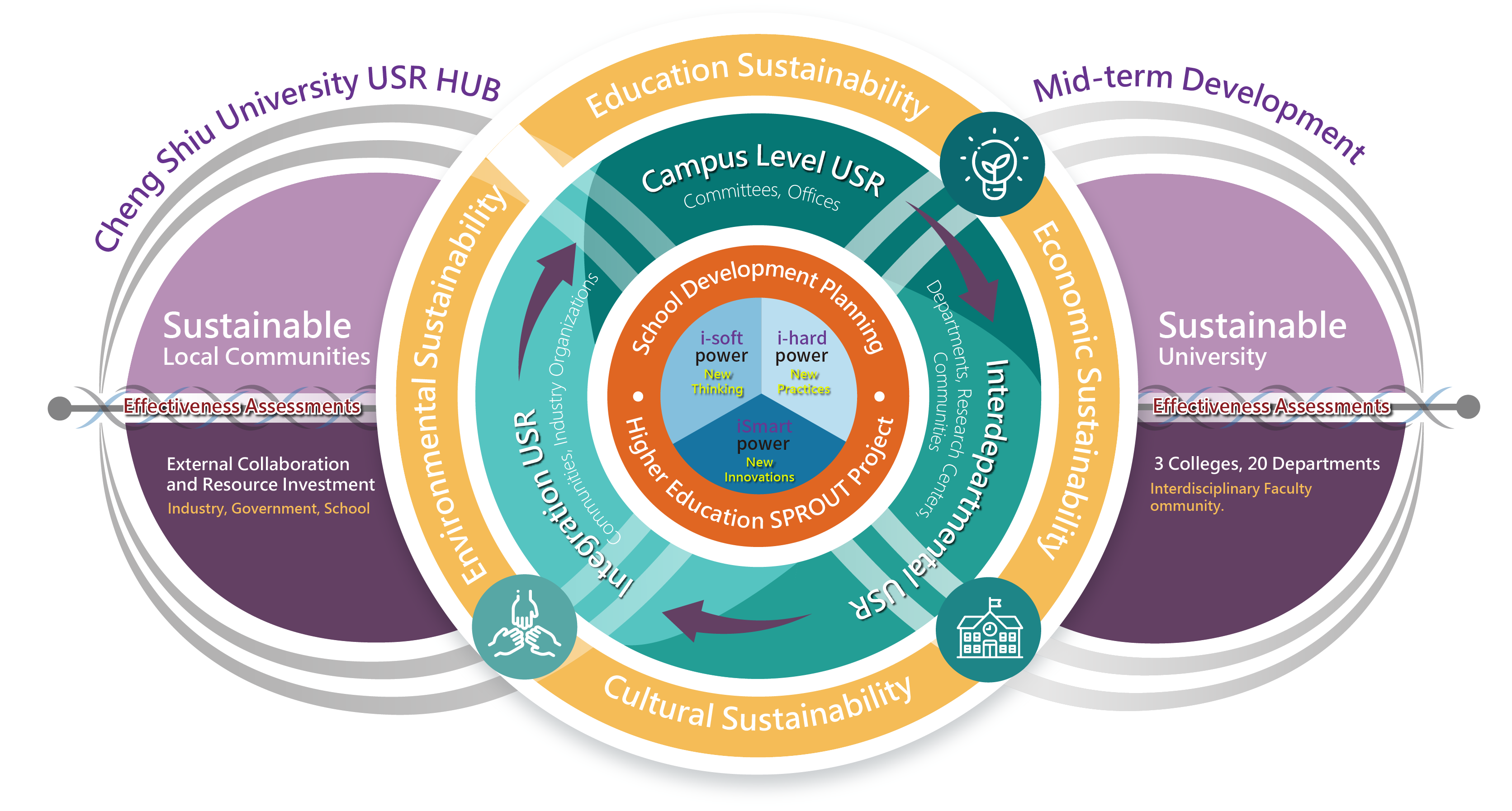
USR Project Implementation and Support Mechanism
The University develops and implements strategies and programs under four core dimensions: Education, Economy, Culture, and Environment. Projects are categorized into three levels—Nursery, Seed, and Sprout—based on their completeness and maturity.
Performance outcomes are monitored by the Office of Social Responsibility and Sustainability, which oversees both project evaluation and budget review. Based on annual results, projects may apply for advancement to a higher level in the following year.
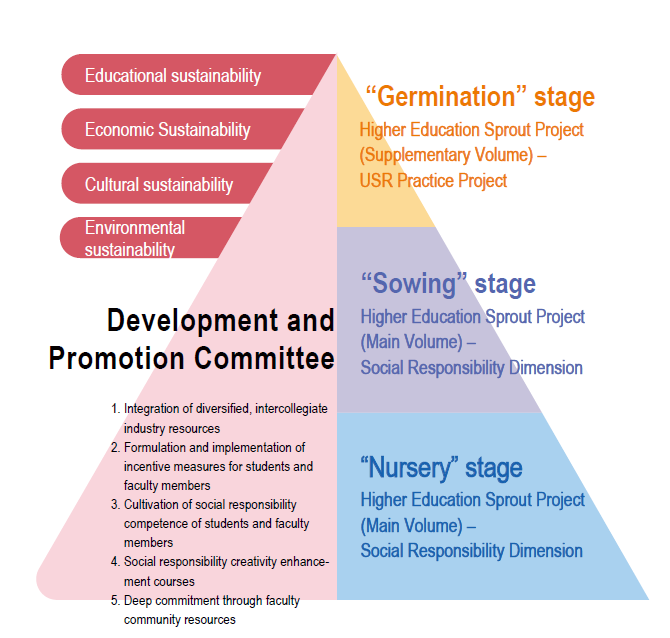
CSU’s USR Project Hierarchical Framework
|
|
|
Level 3 |
Sprout Stage |
Higher Education Sprout Project (Supplementary Volume) – University Social Responsibility (USR) Practice Project |
|
|
Level 2 |
Seed Stage |
Higher Education Sprout Project |
|
|
Level 1 |
Nursery Stage |
|||
Number of USR Projects
USR-Related Budget Allocation, 2022–2024 (Unit: NT$10,000)
|
Item |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
|
University Social Responsibility (USR) Project |
1,485 |
1,246 |
1,155 |
|
Higher Education Sprout Project (Main Volume) – Social Responsibility |
710 |
1,175 |
1,014 |
|
Higher Education Sprout Project (Supplementary Volume) – Student Assistance Mechanism |
78 |
92 |
98 |
|
MOE Subsidy for the Overall Development of Private Universities |
497 |
577 |
351 |
|
Others (e.g., Industry–Academia Collaboration) |
- |
290 |
330 |
|
Total |
2,771 |
3,382 |
2,949 |
Historical Investment in USR-Related Programs (Unit: NT$10,000)
USR Core Dimensions
|
|||
|
Seed Stage Projects |
● Urban Senior Multi-Growth Program ● Silver Health And Intergenerational Co-Learning Program |
Responsible unit |
College of Living Creativity |
|
Nursery Stage Projects |
● Local Talent Development Program – 3 Projects (Social Practice Courses, Volunteer Service, Community Benchmark Learning) ● Cross-Age Diverse Education Program – 4 Projects (Rural Digital/Health Education, Early Childhood Sustainability/Bilingual Education) ● Dementia Care and Health Promotion Program |
Responsible unit |
Office Of Academic Affairs; Office Of Student Affairs College Of Engineering; College Of Living Creativity |
|
|||
|
Seed Stage Projects |
● Rural Agricultural Development Program ● Local Industry–Academia Linkage Program |
Responsible unit |
College of Health and Management; |
|
Nursery Stage Projects |
● Agricultural Innovation and Value-Added Promotion Program ● Brand Taoyuan Aiyu Rural Development Program ● International Civic–Industry Co-Prosperity Program |
Responsible unit |
College of Health and Management; |
|
|||
|
Seed Stage Projects |
● Harbor City Heritage Learning Program ● Aesthetic Education and Cultural Preservation Program |
Responsible unit |
Center for General Education; Conservation and Research Center |
|
Nursery Stage Projects |
● University Support and Local Care Program ● Traditional Folk Performance Culture Promotion Program |
Responsible unit |
Office of Academic Affairs、Sports Center |
|
|||
|
Seed Stage Projects |
● Sustainable Development Program for Industrial Cities |
Responsible unit |
Center for Environmental Toxin and Emerging-Contaminant Research |
|
Nursery Stage Projects |
● Innovative Green Planting and Sustainable Living Program ● Niaosong Environmental Education Implementation Program ● Plastic Reduction and Sustainable Living Program ● Carbon Reduction Education and Campus Practice Program |
Responsible unit |
College of Life and Creativity |
USR Practice Plan
Sprout Stage Projects
In 2024, the University implemented four “USR Budding Projects” under the Ministry of Education’s University Social Responsibility program. Led by faculty teams, these projects mapped local resources and issues across the Kaohsiung–Pingtung region, including Qishan, Linyuan, and Qijin Districts in Kaohsiung and Xinpi Township in Pingtung. Focusing on community care, industry linkages, and environmental sustainability, the projects integrated courses and external resources to jointly promote regional development.
|
|
|
|
|
| Project Name | ||
| Origin |
|
|
|
SDG |
|
|
| Strategy |
Strategy 1: Employment and Entrepreneurship through Skills Training Strategy 2: Passing on and Understanding Local Talents in Cijin Strategy 3: Integration and Cooperation through Respect and Inclusion |
|
| Highlights |
● Skills Training for Employment and Entrepreneurship: Expanded certification programs beyond Chinese cuisine to include caregiving, beauty, nail, and eyelash services, enhancing job and entrepreneurship opportunities for new residents. Leveraged local ingredients to develop creative cuisine, promote micro-entrepreneurship, and bridge cultural dietary differences. ● Talent Inheritance and Understanding: Launched the Shining Light mentorship program with 1,120 service hours, supporting second-generation immigrant children’s development through the “168 Shinguang Team.” Organized food culture exchanges and the Home ATM project, offering Southeast Asian dishes by international students, and fostering cultural understanding through international volunteering. ● Integration through Respect and Cooperation: Strengthened Mandarin learning for new residents, produced 12 life-story episodes to promote cultural exchange, and developed “Jindian Fish Sauce” with local flavors, repurposing marine resources to revitalize Cijin’s fishing village industry. ● 2024 Outcomes: 32 USR innovative courses; 1,999 student enrollments; 39 stakeholders/partners engaged; 7 certification classes; 3 new resident restaurants supported; and 200 hours of Mandarin courses delivered. International Exchange International Exchange on The Fish Sauce Industry In 2024, the University conducted field visits and technical exchanges in Akita, Japan, and Hanoi, Vietnam. By drawing on Japan’s brewing expertise, the project enhanced Taiwan’s fish sauce production and quality, strengthening the “Jindian Fish Sauce” brand. These efforts deepened Taiwan–Japan and Taiwan–Vietnam partnerships, promoted technology transfer and knowledge sharing, expanded access to Southeast Asian markets, and fostered regional industry–academia collaboration and supply chain integration. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Project Name | ||
| Origin |
|
|
|
SDG |
|
|
| Strategy |
Strategy 1: Scientific Testing for Food Safety Strategy 2: Value-Added Marketing of Local Products Strategy 3: Elderly Care and Health Promotion Strategy 4: Talent Development for Linyuan’s Sustainability |
|
|
Highlights |
● Upgrading Aquaculture Value Chains: Assisted farmers with regular seawater quality testing (e.g., dissolved oxygen, temperature, pH, conductivity, salinity) and random sampling. Standardized response procedures help mitigate risks from poor water quality and environmental issues, improving aquaculture yield. ● Value-Added Food Processing: Enhanced sales and productivity of local agricultural and fishery products by ensuring food safety and supporting product development through processing, increasing overall value. ● Revitalizing Idle Spaces for Shared Learning: Transformed the USR base into an Experiential Co-Learning Hub for elderly engagement, offering diverse local courses to strengthen participation and inclusiveness. ● 2024 Achievements: 9 USR innovative courses (955 enrollments), 22 stakeholders/partners engaged, 30 product and water tests conducted, 35 elder-care courses held, and 266 youth volunteers trained. Sustainable Environment Ensuring Food Safety Through Testing and Consulting In 2024, the University assisted Linyuan with 19 tests, covering aquaculture and groundwater heavy metals (3 each), drug residues in aquatic products (6), heavy metals in aquatic products (6), and agricultural produce heavy metals (1). Professional consulting, improvement guidance, and long-term monitoring were provided, building a systematic data framework. Special testing targeted malachite green and crystal violet, two banned aquaculture drugs with antibacterial properties. Through strict and regular monitoring, the project safeguarded food safety, helped farmers avoid violations, ensured product quality, and strengthened both industry reputation and community health for sustainable development. |
|
|
▲Supporting Agricultural and Fishery Producers in Product Development |
▲Summer Camp on Food Safety and Environmental Awareness
|
|
|
| Project Name | ||
| Origin |
|
|
|
SDG |
|
|
| Strategy |
Strategy 1: Agricultural Value-Adding through Brand Marketing Strategy 2: Leisure and Tourism – Enjoy Xinpi Strategy 3: Youth Employment – “Food in Xinpi” Initiative |
|
| Highlights |
● Upgrading Aquaculture Value Chains: Assisted farmers with regular seawater quality testing (e.g., dissolved oxygen, temperature, pH, conductivity, salinity) and random sampling. Standardized response procedures help mitigate risks from poor water quality and environmental issues, improving aquaculture yield. ● Value-Added Food Processing: Enhanced sales and productivity of local agricultural and fishery products by ensuring food safety and supporting product development through processing, increasing overall value. ● Revitalizing Idle Spaces for Shared Learning: Transformed the USR base into an Experiential Co-Learning Hub for elderly engagement, offering diverse local courses to strengthen participation and inclusiveness. ● 2024 Achievements: 9 USR innovative courses (955 enrollments), 22 stakeholders/partners engaged, 30 product and water tests conducted, 35 elder-care courses held, and 266 youth volunteers trained.
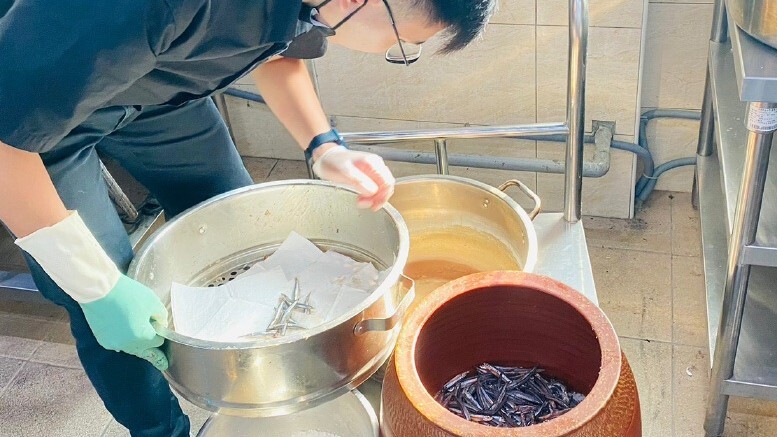
Collaborating with Enterprises and Small Farmers to Advance Food and Agriculture Sustainability Cheng Shiu University signed an MOU with Hanlai Gourmet and Pingtung Yaguo Agricultural Marketing Cooperative, bridging local farmers with corporate resources to enhance product value. By sourcing premium agricultural products from Xinpi, Hanlai reduced food miles, lowered carbon emissions, and fulfilled its corporate social responsibility. This tripartite collaboration fostered industry upgrading and cross-sector cooperation. Building on the success of the Xinpi Sustainability project, the initiative was elevated in 2025 to the fourth-phase USR Deepening Project, Xinjia Sustainability, extending its scope to Jiadong Township in Pingtung. The project promotes the “Revitalizing Zuodui, Creating a New Jiadong” action plan, integrating tourism, design, and cultural heritage restoration to establish an innovative platform merging culture and gastronomy. |
|
|
|
▲Collaborating with Hanlai Yagu to Create a Win-Win-Win Outcome
|
|
|
University Social Responsibility Practice Sites
Cheng Shiu University has long been rooted in the Kaohsiung–Pingtung region, building on the achievements of the Higher Education Sprout Project (2017–2024) and years of University Social Responsibility (USR) initiatives. Over time, the scope of engagement and the number of project teams have steadily expanded, advancing four dimensions of sustainability: education, economy, culture, and environment. In 2024, the University carried out 17 nursery projects, 7 seed projects, and 4 USR sprout projects, totaling 28 faculty–student teams with the participation of more than 200 faculty members guiding students in local engagement.
To address the growing impacts of extreme climate events and to respond to the strong concerns of faculty and students on net-zero carbon emissions and biodiversity, the University expanded its practice fields in 2024 across 18 districts in Kaohsiung and Pingtung, strengthening its social impact. Building on existing sites and themes, efforts in 2024 focused particularly on environmental and ecological initiatives, fostering team development and project implementation. Through these actions, the University underscores its responsibility in advancing environmental sustainability, aiming to play a leading role in talent cultivation and regional development.
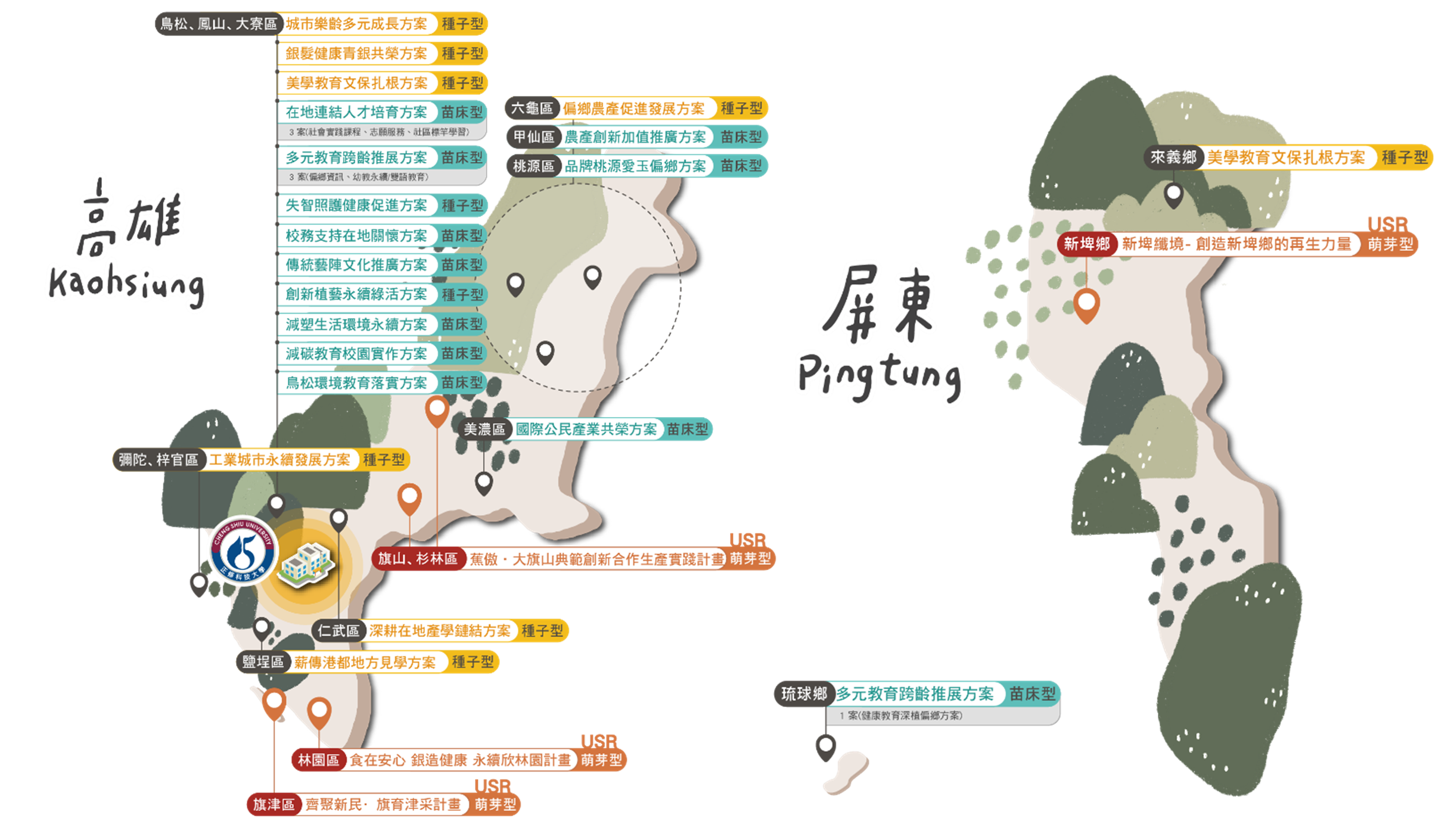 |
USR Practice Sites, 2024
|
Kaohsiung City 15 districts |
Niaosong, Fengshan, Daliao, Mituo, Ziguan, Taoyuan, Jiaxian, Liugui, Meinong, Renwu, Yancheng, Linyuan, Qijin, Qishan, Shanlin |
|
Pingtung County 3 townships |
Xinpi, Laiyi, Liuqiu |
Advancing Impact Evaluation of Social Responsibility Initiatives
To effectively evaluate the implementation of the University’s development policies and strategies, we established an assessment framework built on four core dimensions: institutional governance, talent cultivation, local engagement, and global connection. This framework integrates multiple tools, including institutional databases and surveys, to systematically analyze how resource allocation impacts stakeholders. Through short-term and medium-to-long-term evaluations of social responsibility outcomes, the University continuously refines decision-making and incorporates the findings into its University Development Plan, enhancing both precision and foresight in institutional advancement.
Each March, the University publishes its Annual University Social Responsibility Report, featuring a dedicated section on stakeholder engagement and communication outcomes. The report highlights the progress of performance indicators and the execution of strategic initiatives, showcasing the University’s contribution to regional development. This mechanism supports both a sustainable campus and community, advancing the University’s vision of long-term sustainability.

















